
Beat the jargon with this essential list of fleet terminology, from AARTO to ULEZ and everything in between.
Like any other industry, fleet management comes with its own terms and definitions. While many of these terms have been in use for decades, the evolution of the fleet industry means more definitions are added to the list. We’ve collected the most recent fleet speak here to help you cut through the jargon.
AARTO
The AARTO Act seeks to tackle the problem of road traffic fatalities by imposing hefty fines coupled with demerit-points on driving licences, which leads to the suspension of driving licences where drivers infringe on the law repeatedly. It’s full name is the Administrative Adjudication of Road Traffic Offences (AARTO) Act, No. 46 of 1998, which was approved by Parliament in 1998, was amongst others, created with the view to forge a closer and more effective and efficient link between enforcement and the adjudication process, yet which is still objective, transparent and fair.ACCMAN
Accident Management companies can help reduce accident costs by limiting repair costs and making sure drivers get back on the road again after an accident. It enables fleet managers to highlight drivers needing more training.BBBEE
The Broad Based Black Economic Empowerment system is a tool employed by South Africa to address racial injustices of the past and redress economic imbalances from the apartheid era. The purpose of a BBBEE status is to give the broad spectrum of previously disadvantaged and marginalised people equal access to participate actively and meaningfully in the mainstream economy.
BEE
The Black Economic Empowerment system is a tool employed by South Africa to address racial injustices of the past and redress economic imbalances from the apartheid era. The purpose of a BEE status is to give the broad spectrum of previously disadvantaged and marginalised people equal access to participate actively and meaningfully in the mainstream economy.Benchmarking:
Benchmarking is a performance comparison between multiple organisations. This is done to establish industry standards, such as service delivery, vehicle specifications, fuel usage, financial information and environmental issues.BI
Business Intelligence adds value to fleet management; it is a set of techniques and tools to acquire and transform raw data into meaningful and useful information to analyse a company fleet. The BI technologies are capable of handling large amounts of structured and sometimes unstructured data to help identify, develop and otherwise create new strategic business opportunities. The goal of BI is to allow for the easy interpretation of these large volumes of data. Identifying new opportunities and implementing an effective strategy based on insights can provide businesses with a competitive market advantage and long-term stability. BI technologies provide historical, current and predictive views of business operations.BRN Number
A BRN Number is a business registration number of eight digits.
CO2 emissions
CO2 emissions refers to the levels of carbon dioxide your fleet vehicles release into the atmosphere.Cost-benefit analysis
A cost benefit analysis looks at the potential costs and benefits of a particular strategy or course of action. This helps fleet managers make an informed decision, in order to decide whether or not to proceed with something.CPI
The Consumer Price Index measures changes in the prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services. The annual percentage change in a CPI is used as a measure of inflation. As the cost of fuel increases, the CPI is surpassed. This influences the fleet industry to a huge extent as certain costs related to vehicle maintenance may increase and fleet managers may need to re-evaluate their budget.CPK
Cost per kilometer is the fixed rate per kilometre driven in a car, which accounts for fixed (procurement, finance, insurance, registration, vehicle taxes) and variable (fuel, maintenance, tyres, tracking, etc.) costs divided by the actual kilometers travelled.DCF
Discounted cash flow is commonly used to evaluate the potential for an investment opportunity. It is a method to determine what a business is worth today in light of cash yields in the future. In short, it the valuation method used to present the value of an investment's future cash flows in order to arrive at a current fair value estimate for the investment. If the value arrived at through DCF analysis is higher than the current cost of the investment, the opportunity may be a good one. The sum of all future cash flows, both incoming and outgoing, is the net present value (NPV), which is taken as the value or price of the cash flows in question.FCI
The Fuel Consumption Index is an indication of the amount of fuel a vehicle uses to travel a specific distance at a specific speed. Fuel consumption of new cars is measured on a chassis dynamometer in a closed room, not a wind tunnel.Fit for purpose:
Vehicles that are fit for purpose are designed specifically for the role in which they’re used. For example, a hatchback is not fit for the purpose of transporting hazardous chemicals - it is, however, fit for purpose as a company vehicle for your sales team. To find out if your fleet is fit for purpose, take our fit for purpose survey.Fleet asset register:
A fleet asset register is a comprehensive database of all your fleet information. It includes information such as vehicle type, registration numbers, date of acquisition; Vehicle licence details; licence expiry date; BRN number the vehicle is registered under with e Natis; Original purchase price; petrol or diesel derivative; pool vehicle or allocated to a driver; Service or Maintenance Plan; extended Warranty and the current mileage of the vehicle. This information can be stored electronically in your fleet maintenance software to enable the linking of vehicles to drivers; insurance details, accident history and operational items It is important that your fleet asset register is kept up to date.
FML/FMR:
A Full Maintenance Lease is a fixed monthly premium determined by the choice of vehicle, period of usage and kilometres travelled. A full maintenance rental is also an off balance sheet transaction, identical to the operating rental but with a fixed maintenance plan. It is a comprehensive fleet management solution offered at an agreed rental.FMR
A Full Maintenance Rental is an off balance sheet transaction, identical to the operating rental but with a fixed maintenance plan. Customers can outsource the finance, maintenance risk and costs of their fleet, ensuring a fixed expenditure for efficient budget control.HCV
A Heavy Commercial Vehicle has a gross combination mass of over 7.5 tonnes. In order to cross borders, HCVs must not exceed 40 tonnes laden weight in South Africa.HP
Vehicle hire purchase is a very simple type of car hire plan. After paying a fairly low deposit, you hire a vehicle with the option to buy it from the lessor by the expiration of the contract. A company acquires an asset by paying monthly instalments (cost + interest of the asset) over a period of time or term for a contract.IRR
Private equity firms like oil- and gas companies use the internal rate of return to compare the relative attractiveness of investments. Projects with the highest IRRs are considered the most attractive and are given a higher priority. It is a metric used in fleet management measuring the profitability of potential investments. The IRR can typically be of significant value to any fleet company looking to grow, invest, improve infrastructure and/or retain working capital and lines of credit for key organisational needs. IRR is a discount rate making the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows from a particular project equal to zero. IRR calculations rely on the same formula as NPV does. Use the following formula to calculate NPV: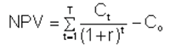
LCV
Light Commercial Vehicles is the official term in South Africa for commercial carrier vehicles (a bakkie, for example) with a gross weight of 3.5 tonnes.Lessee
A customer leasing products from lessor and thus holds the lease of an asset. In fleet management, it is required that the lessee must keep the vehicle in service for a minimum number of months.Lessor:
The leasing company/person who leases or lets an asset to another.MCV
Medium Commercial Vehicles generally refer to vehicles between 3.5 and 7.5 tonnes, like various trucks and vans.MM
Managed maintenance enables fleet managers to retain the maintenance risk and utilise a maintenance department to control and minimise vehicle maintenance and repair costs in line with the fleet budget or policy.OCR
An Optimal Character Recognition (OCR) software, enables the fleet industry to capture the traffic violation fee details automatically and carry out the entire fines redirection process based on customer specific rules. The software enables scanning of VIN numbers and converts images to text for a more robust reporting. It is the mechanical or electronic conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photograph of a document, a scene-photo (e.g. the text on signs and billboard in a landscape photograph) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image.OEM
The Original Equipment Manufacturer is the original producer of a vehicle’s components used in another company’s end product. OEM vehicle parts are identical to the parts used in the production of the vehicle.OPL/OPR
The Operating Lease, now more commonly known as Operating Rental, offers the lessor the option to use the vehicle for an agreed period and mileage, the risk associated with the maintenance; tyres and servicing remains with the lessee. As with the Full Maintenance Rental, the Operating Rental allows the use of an asset, but does not convey the rights to ownership of an asset.
OL
The Operating Lease is a leasing solution where selected vehicles are used at an agreed rental over a set period of time. It allows the use of an asset, but does not convey the rights to ownership of an asset.Optimum replacement cycle:
Your optimum replacement cycle refers to a vehicle’s lifespan - taking into account at what point a vehicle’s maintenance costs start to outweigh the benefits of retaining the vehicle. The optimum replacement cycle on fleet vehicles is generally the period that the vehicle is covered under its manufacturer warranty. Your optimum replacement cycle should ensure that a new vehicle is ordered in time to replace the old one, so that your fleet is never stuck without a vehicle.OR
A fleet company’s operating rental is structured as an off balance sheet transaction, in which fleet managers take full risk in terms of the residual value of the vehicle at the end of the lease period. This solution is designed for companies who need vehicles to operate their business but don’t want to place an unnecessary burden on their asset base. It allows companies to rent vehicles for a fixed period of time while taking advantage of tax recoveries and transfer the risk at the end of your contract.ORT
Open Road Tolling is a method of electronic toll collection along a road or road network. Vehicles should be fitted with an eTag, which can be acquired on a pre-paid basis or linked to an account, this method of collection allows for the motorist to make use of a road or road network without stopping at a Toll Plaza or Toll barrier points for the manual collection of monies. Motorists can drive along their route without stopping, as all billing is electronic.”
RCO
The real cost of ownership is a comprehensive consideration of hard and soft costs over the lifetime of a vehicle.Residual value:
The residual value of a vehicle is what it’s worth at the end of its lifespan.Return on Equity
Net income/Shareholder's equity
ROCE
Return on capital employed is a financial ratio that measures a company's profitability and the efficiency with which its capital is employed. It is calculated as: ROCE = Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT)/Capital Employed, and is essential to fleet managers so they can track the efficiency of their fleet. “Capital Employed” as shown in the denominator is the sum of shareholders' equity and debt liabilities; it can be simplified as (Total Assets – Current Liabilities). Instead of using capital employed at an arbitrary point in time, analysts and investors often calculate ROCE based on “Average Capital Employed,” which takes the average of opening and closing capital employed for the time period.ROE
Return on Equity measures how well an investment into a specific division is utilised. It is the amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholders equity. Return on equity measures a corporation’s profitability by revealing how much profit of a company generates the money shareholders have invested. ROE is expressed as a percentage and calculated as:Return on Equity = Net income/Shareholder’s Equity
ROI
Return on Investment calculates the profits of an investment as a percentage of the original cost. It measures how much money was made on the investment as a percentage of the purchase price. It acts as a performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. ROI measures the amount of return on an investment relative to the investment’s cost. To calculate ROI, the benefit (or return) of an investment is divided by the cost of investment and the result is expressed as a percentage of a ratio.The return on investment formula is calculated as follows:
![]()
Route optimisation
Route optimisation ensures that your drivers follow the most cost effective routes. This looks at how to limit trips and minimise mileage where possible. Commercial route planning software can help to plan routes for fleets that need to plan complex journeys.RPK
The cost per kilometre calculated in South African rands.SAVRALA
South African Rental and Leasing Association is the representative voice of South Africa’s vehicle rental, lease and fleet management sector and offers information on how to rent or lease a vehicle.SLA
A service level agreement is a useful tool to manage the relationship between a service provider and their client. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract.TCO
The total cost of ownership is designed to get the most out of your fleet budget by identifying and optimising the costs associated with running your vehicles including taxes, fuel consumption, fines, etc. It is a financial estimate intended to help buyers and owners determine the direct and indirect costs of a product or system. It is a management accounting concept that can be used in full cost accounting.Tendering
Tendering is the process of inviting bids from various suppliers, to provide fleet vehicles or services. Each supplier will provide a tender document in which they will outline their value proposition, and give a breakdown of the vehicles or services which they will provide.ULEZ
The Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) is an area within which all cars, motorcycles, vans, minibuses, buses, coaches and heavy goods vehicles (HGVs) will need to meet exhaust emission standards (ULEZ standards) or pay a daily charge to travel.This is an overview of the most common terms used in in the fleet industry. We’ll be posting more information on what fleet management can do for you, so sign up to our blog below to receive relevant fleet insights.

